The global business community has been in a reputation freefall for the past couple of years, with trust in corporations experiencing the most significant regression since the end of the Great Recession. Not only has this crisis of confidence rattled some of the world’s largest companies and the leaders who sit at their helms, but countries are feeling the effect too.

“People are expecting more and more from companies and countries, in terms of solving the challenges we’re seeing around the world, and they’re being let down,” says Nicolas Georges Trad, executive partner at the Reputation Institute, a reputation measurement and management services firm. Since 2008, the institute has published the Country RepTalk, an annual study of nations’ reputations. This year’s ranking revealed an average one-point decline in the reputation of Country RepTrak nations.
“There’s been a lot of disruption in the world in the last 18 to 24 months,” adds Stephen Hahn-Griffiths, the institute’s chief reputation officer. “It really adds up to a lingering feeling of uncertainty in the world at the intersection of geopolitical tension, nationalism and underlying social unrest.”
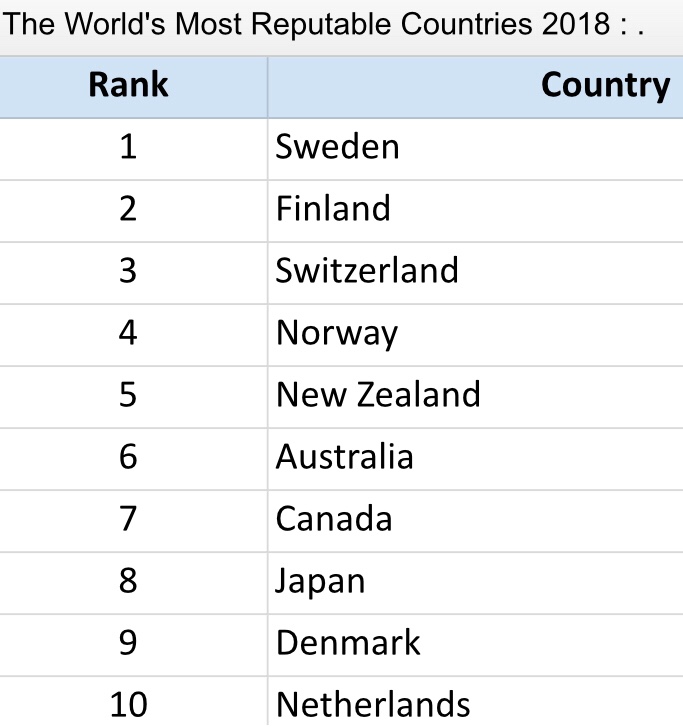
To determine the Country RepTrak, the institute surveyed more than 58,000 individuals in Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom and the United States during the period from March to April 2018. The 55 countries considered were those with the greatest gross domestic product and familiarity with at least 51% of the G8 general population.
While financial stability has always influenced reputation, just two of the world’s top economies secured spots in the Country RepTrak’s top 10, with Canada falling from first place to No. 7 and Japan rising four spots to No. 8. And a country’s size doesn’t seem to matter either: None of the most populous nations and only two of the geographically largest—Australia (No. 6) and Canada—managed to break into the upper echelon. Instead, characteristics such as beautiful landscapes, friendly citizens and ethical policies are driving nations’ reputations. “A new and significant trend that is emerging is altruistic happiness,” says Hahn-Griffiths. “The countries that rise to the top of the rankings are the ones that allow you to fulfill the pursuit of happiness.”
One example of this new trend is Sweden, which climbed two spots to No. 1, with a score of 81.7. The Scandinavian nation is no stranger to the top ranks of the Country RepTrak, having claimed the top position for the first time in 2016. Its excellent reputation can, in part, be credited to its decades of sustainability initiatives, dating back to 1967, when Sweden became the world’s first country to form an environmental protection agency. Since then, green living has been a priority, and it looks to be paying off: Today, more than 99% of all waste is recycled and 52% of energy production is generated by renewable resources. Globally, Sweden accounts for less than 0.2% of all greenhouse gas emission.
Sweden has also become synonymous with hospitality. The country of 10 million has a long history of embracing the displaced, most recently opening its borders to 163,000 refugees of the Syrian Civil War—more per capita than any other European nation. “Uncertainty is making countries focus more inward than outward,” says Georges Trad, pointing to countries like the United States as an example of this. At No. 34, the U.S. has barely recovered from last year’s 10-spot dive to No. 38, the result of President Trump’s election and of anti-immigration rhetoric. “Closing borders is not looked upon favorably.”
Just as the Swedes have welcomed immigrants, they have also supported the LG TQ community—legalizing same-sex marriage in 2009 and adding sexual orientation discrimination protections to its constitution in 2011—and women. Sweden has never ranked lower than fifth place on the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report report, and it was the first country to replace maternity leave with parential leave (in 1974). Its paid-leave policy is one of the world’s most generous, offering parents 480 days of leave up until a child’s eighth birthday. While the country still has work to do—Swedish women make just 88 cents for every dollar banked by their male counterparts—the government is transparent about its shortcomings, openly reporting on the stetae of gender equality.
The Swedish way of life is really aligned with the pursuit of happiness,
“The Swedish way of life is really aligned with the pursuit of happiness,” says Hahn-Griffiths. “But it didn’t just happen by chance.”
Sweden ranks only a few tenths of a point above Finland (No. 2) and Norway (No. 4), neighboring Nordic nations with their own progressive policies, and it is interesting to consider the reasons for this. It all comes down to compelling storytelling, according to Stephen Hahn-Griffiths. “The challenge for countries, as opposed to corporations, is there are many voices,” he says, “different groups communicating narratives that might not align. What Sweden has done is develop one narrative that everyone speaks from.”
The narrative, called “Sharing Sweden,” is outlined in a 12-page manual, produced and promoted by a public agency called the Swedish Institute. The strategy speaks to “core values” and “target groups,” not unlike a business plan. “Reputation has to do with creating a balance between reality and perception,” notes Georges Trad.
The 29 nations with declining reputations would do well to take note of Sweden’s narrative strategy. Take Russia, for instance, which dropped one spot to No. 52. “St. Petersburg is beautiful, but that’s not the image that comes to mind when you think of Russia. It’s Putin and a country that’s flexing its economic muscles. That beauty is not being communicated by the country, the media or the general public,” says Hahn-Griffiths. “That sense of happiness and altruism is what matters in defining a country’s reputation.”
Source: Forbes
Yet to be decided is what will happen on exit day, the divorce deal and final destination
Theresa May’s efforts to thrash out a position on what kind of future ties the UK wants with the EU have been hobbled by deep divisions within the cabinet.

Britain is nearing the final straight of Brexit. At 11pm local time on March 29 2019, the UK is scheduled to leave the bloc. But still to be decided is what precisely will happen on Brexit day, what kind of deal, if any, Britain will leave with, and the final destination of the negotiations.
Some of the biggest questions could come to a resolution before the summer is out.

Two years after the UK’s historic June 23 2016 vote to leave the EU, the Financial Times sets out the chief way stations on the road to Brexit and beyond.
June 28 to 29: EU summit
The EU had high hopes of resolving one of the most difficult issues in negotiations before the June summit: the “backstop” arrangement to avoid a hard border on the island of Ireland if other approaches do not work.
But the talks have made limited progress, with the two sides deadlocked over how integrated Northern Ireland would remain with the EU and what trade barriers would emerge along the Irish Sea. Negotiators made more headway in other parts of the withdrawal treaty. Still, the EU sees the negotiating delays as increasing the risks of a no-deal Brexit.
Early July: Cabinet tries to agree white paper at Chequers summit
For months, Theresa May’s government has sought to thrash out a position on what kind of future ties it wants with the EU after Brexit. Its efforts have been hobbled by deep divisions within the cabinet and the ruling Conservative party. The white paper spelling out the UK plans has been delayed several times. The full cabinet is likely to meet to try to come to an agreement at Chequers, the prime minister’s country residence, around July 4 and 5.
July 15 (at the latest): Customs union vote
Andrea Leadsom, the leader of the House of Commons, says long-delayed trade and customs bills will be debated by MPs by mid-July. An amendment to the trade bill backed by Conservative Brexit rebels and in line with Labour party policy calls for the UK to stay in a customs union. The government resists this but is far from certain of victory.
September: Immigration report
The deadline for a government-requested report on European migration to the UK. The report, which is being drawn up by the UK’s Migration Advisory Council, is intended to provide evidence for the design of a new, post-Brexit migration system.
September 30 to October 3: Conservative party conference in Birmingham
The annual gathering of the Tory faithful will be the last before Britain is scheduled to leave the EU. It may well constrain Mrs May from making concessions to the EU for fear of upsetting Brexit hardliners.
October 18 to 19: EU summit
The October summit had been seen in the past as the most likely opportunity for a final agreement on the UK divorce from the bloc and a statement on future relations. But it will come just two weeks after the Conservative conference, restricting Mrs May’s room for manoeuvre without antagonising Conservative party Brexit hardliners.
November: Emergency EU summit?
A further EU summit could be needed to finalise the divorced deal if the deadlock on Ireland continues in October.
December 13 to 14: The last European Council of 2018
This is widely seen as the last practical date for an Article 50 divorce deal to be signed off by Britain and the EU. The summit comes a little over three months before the UK’s scheduled departure.
January to February 2019 (at the latest): Commons approval
By now the House of Commons must approve whatever Brexit deal Mrs May agrees in Brussels. Parliament must also pass an Implementation and Withdrawal Bill that sets out the terms of Brexit in fuller detail.
Until March 29 2019: Ratification
To take effect, the withdrawal agreement needs to be backed at an EU summit by a supermajority of leaders of member states (representing at least 15 of the other 27 EU countries and 65 per cent of their population). That decision must also be approved by the European Parliament in a plenary vote. Any legally questionable elements of the withdrawal treaty could also be referred to the European Court of Justice by MEPs.
March 29 2019: Brexit day
There will be plenty of political declarations on this historic day. But whether there will be discernible changes to everyday life at the moment of the UK’s departure from the EU depends on the negotiations in the preceding months. They could produce a largely seamless transition or, if they fail to yield any deal, a much more chaotic “cliff edge” Brexit.
After March 30 2019: Trade talks and transition
Full-fledged trade talks can now begin between the UK and the EU. While Britain remained a member state, such talks were not permitted under EU law. Under the deal reached in principle in 2018, this is when the 21-month transition period begins. During this time most aspects of UK membership of the EU will remain in place, including free movement across borders and membership of the customs union and single market. But Britain will no longer have a vote.
December 31 2020: An end to transition?
The transition period is scheduled to end on this date. But some EU negotiators also doubt that a full UK-EU trade deal will be agreed by now — or for some time to come — given the protracted nature of such talks. That is one reason why the EU insists on “backstop” provisions to avoid a hard border in Ireland that will last unless and until a new arrangement is implemented.
December 31 2021: Goodbye to the backstop?
The UK government says it expects that any “temporary customs arrangements” introduced as part of the backstop would cease by this time because alternative measures will have been put in place. The EU is highly sceptical and says no time-limit on the backstop is acceptable.
Mid 2020s: Journey’s end?
Many business leaders suggest that the “maximum facilitation” plan favoured by Brexiters — relying on advanced technology to speed-up customs clearances — would need years to put in place, delaying “full Brexit” until deep into the 2020s. A less ambitious “fast track” system on the US-Canada border took decades to develop and billions of dollars in investment.
Source: FT
Today it is Midsummer Eve, the biggest annual holiday of Sweden.
This is when the day is as longest in the year and it is basically daylight 24/7.

Al Sweeish people get together with damily and friends to celebrate this day with a specific Midsummer meal including; herring, potatoes, meatballs, sausages and a special cold sour sauce – followed by strawberries with cream. All accompanied by beer and a lot of vodka.
To all friends and all readers of this blog: Happy Midsummer 2018!






You must be logged in to post a comment.